What is hvls fan?
What is an HVLS Fan?
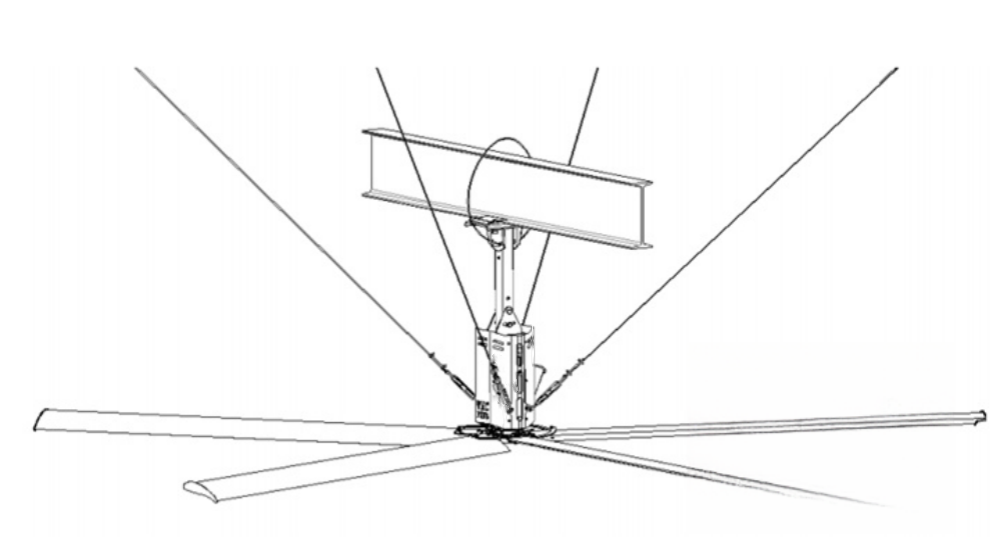
An HVLS fan is a large-diameter ceiling fan, typically ranging from 7 to 24 feet, designed to move large volumes of air at low rotational speeds. These fans push a column of air downward, which disperses along the floor, creating a uniform airflow pattern known as “horizontal floor airflow.” This air distribution is particularly effective in high-ceiling spaces, addressing discomfort and inefficiencies caused by stagnant air and underperforming HVAC systems.
Major Applications of HVLS Fans
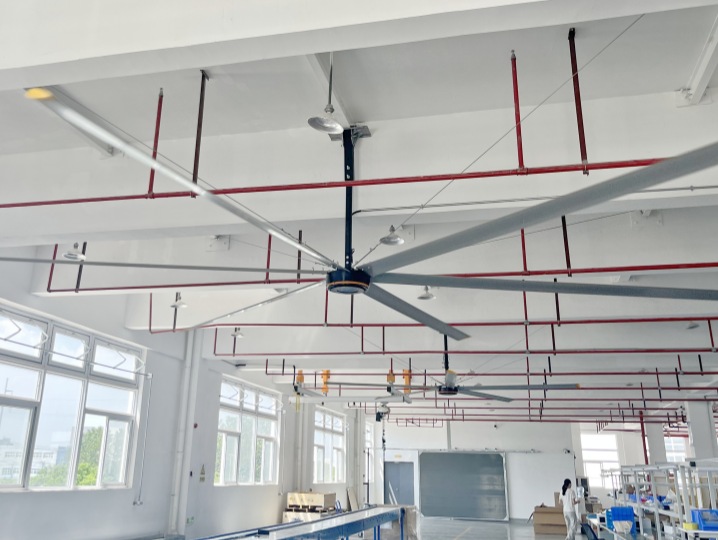

Enhancing Comfort
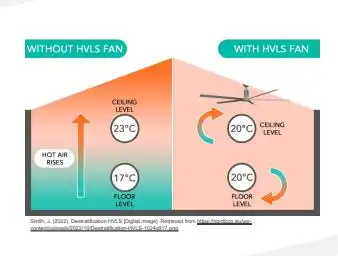
HVLS fans are commonly used to create a comfortable environment by increasing airflow. They circulate air gently and consistently, which enhances evaporative cooling and reduces perceived temperatures. During winter, HVLS fans redistribute the warm air trapped near the ceiling, eliminating thermal stratification and improving temperature uniformity from floor to ceiling, reducing heating demands.Saving Energy
HVLS fans significantly reduce energy consumption. In summer, they allow thermostats to be set a few degrees higher without compromising comfort, alleviating the load on air conditioning systems. In winter, by redistributing warm air, they help lower heating costs. This dual functionality makes them an energy-saving choice for large spaces.Improving Indoor Air Quality
In environments prone to dust and airborne particles, such as warehouses and agricultural facilities, HVLS fans disperse stagnant air and improve ventilation. This leads to better air quality, directly benefiting workers' health and productivity.
Technical Considerations for Choosing HVLS Fans
Fan Size and Airflow
The size of the fan is critical in determining its air delivery capacity. Larger-diameter HVLS fans can cover more area, reducing the number of fans needed. For example, a 24-foot HVLS fan can cover approximately 20,000 square feet. However, selecting the appropriate fan size requires consideration of ceiling height, room dimensions, and specific airflow needs.Airflow Efficiency
The efficiency of an HVLS fan is often measured in cubic feet per watt (CFM/W). Efficient fan designs aim to deliver maximum airflow with minimal energy consumption. Modern HVLS fans can achieve remarkable efficiency levels, with some delivering up to 360,000 cubic feet of air per minute at just 1.5 kilowatts.Motor Type and Drive System
HVLS fans are typically powered by either direct-drive or gear-driven motors. Direct-drive motors are generally more efficient and quieter, while gear-driven systems, although cheaper, may require more maintenance due to gear wear. Motor efficiency directly impacts energy consumption and the fan’s longevity.Installation and Maintenance
HVLS fans must be installed with proper clearance from structural elements and HVAC systems. The installation process should ensure optimal airflow without interference from walls or other obstacles. While maintenance requirements for HVLS fans are typically low, regular inspections are essential to keep them running at peak performance.
HVLS Fans and Energy Efficiency Regulations
In recent years, energy efficiency regulations have recognized the significance of HVLS fans in large spaces. For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) has established minimum energy efficiency standards for large-diameter ceiling fans, including HVLS fans. These standards are based on metrics like the Ceiling Fan Efficiency Index (CFEI), which helps compare fan performance at various speeds. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) also includes HVLS fans in its energy efficiency guidelines, emphasizing their role in reducing commercial building energy consumption.
The Future of HVLS Fan Technology
As energy efficiency becomes a core driver in building design, HVLS fans are poised to play a more significant role in the future. Innovations in motor technology, such as permanent magnet motors, promise to enhance fan efficiency further. Additionally, the integration of smart control systems with Building Management Systems (BMS) will enable facility managers to monitor and optimize fan performance in real-time.
Advancements in Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) modeling allow engineers to better predict airflow patterns, optimizing HVLS fan placement in new constructions and retrofitting projects. This leads to greater energy savings and improved comfort.
 New Year Holiday Notice
New Year Holiday Notice
 Large Ceiling Fans: The Soluti
Large Ceiling Fans: The Soluti
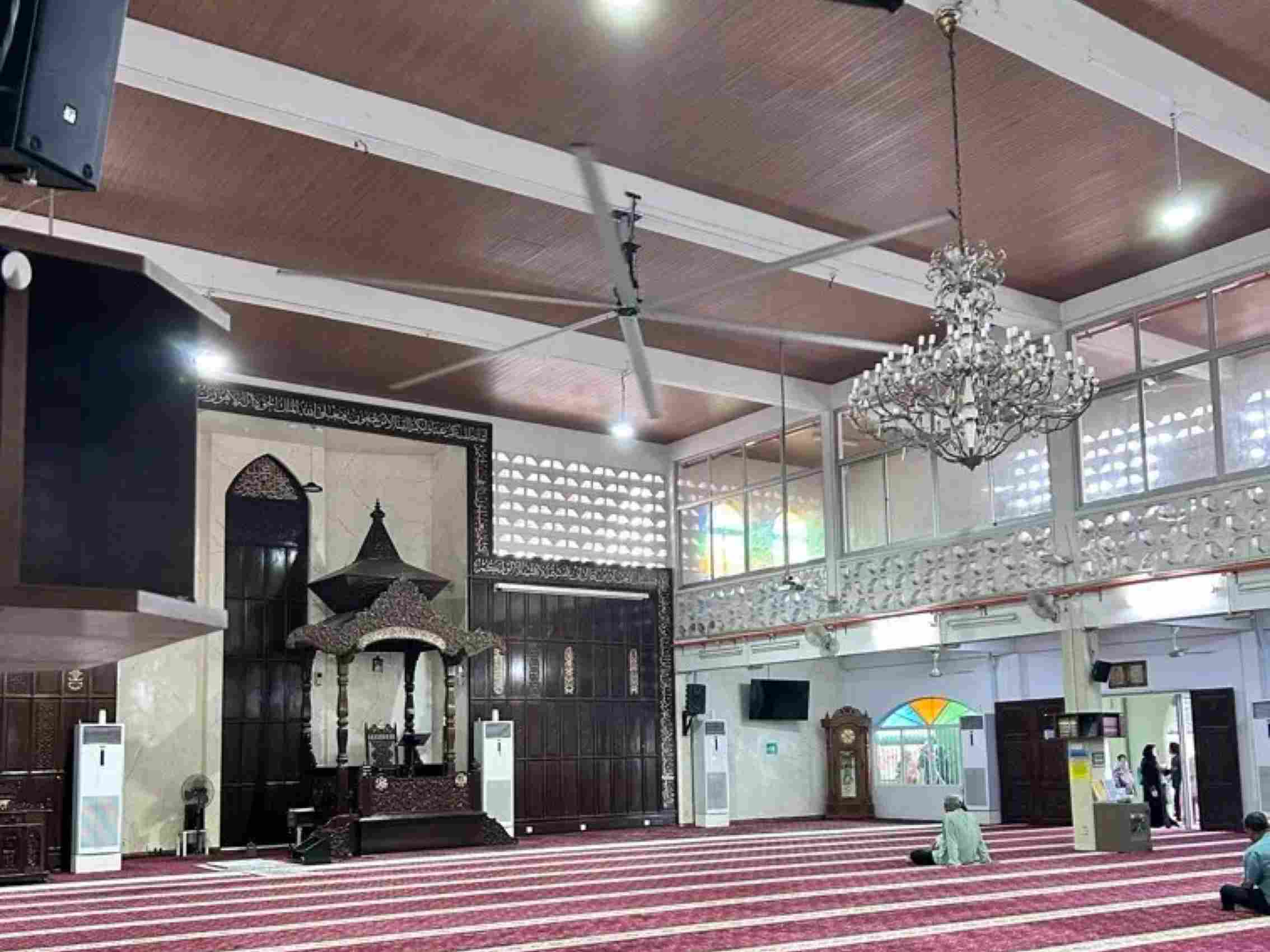 Enhancing Public Comfort with
Enhancing Public Comfort with
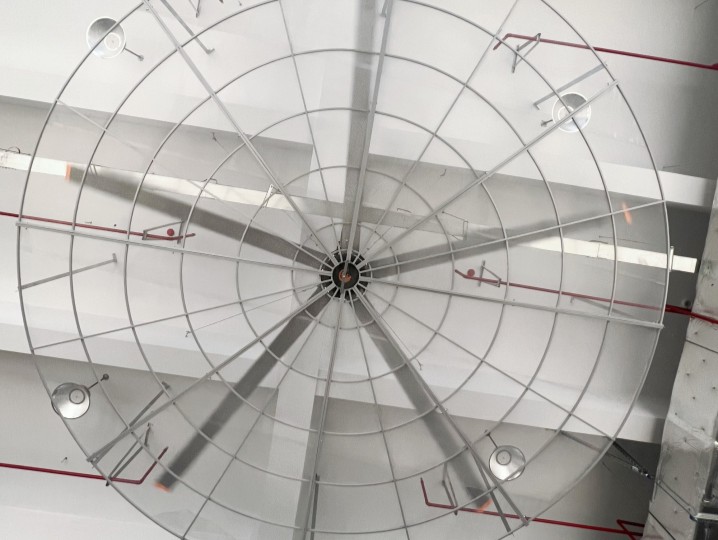 Fall Prevention Measures for L
Fall Prevention Measures for L
